# 数据结构与算法 (DataStructureAndAlgorithms)# 注意事项
该笔记使用 C++、开发环境为 VS2022
该笔记较少使用大量书面语言和数学证明去描述一些算法,因此不适合正规入门使用,也不适合考试使用
# TestArrCreate作用:生成一个测试数组,用于测试代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #pragma once #include <iostream> #include <ctime> #include <cstdlib> #include <vector> using namespace std;class testArr { public : testArr (); ~testArr (); int * arr; int arrLen; void createArr () void printArr () };
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 #include "testArr.h" void testArr::createArr () this ->arrLen = rand () % 5 + 5 ; this ->arr = (int *)malloc (this ->arrLen * 4 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < this ->arrLen; i++) { arr[i] = rand () % 300 ; } } testArr::testArr () { srand ((unsigned )time (NULL )); this ->createArr (); } testArr::~testArr () { if (this ->arr != NULL ) { delete [] this ->arr; this ->arr = NULL ; } } void testArr::printArr () for (int i = 0 ; i < this ->arrLen; i++) { cout << this ->arr[i] << " " ; } }
# 算法、复杂度:算法 (Algorithm) 是为了解决某类问题而规定的一个有限长的操作序列。
一个算法必须满足以下五个重要特性:
(1) 有穷性 。一个算法必须总是在执行有穷步后结束,且每一步都必须在有穷时间内完成。
(2) 确定性 。对千每种情况下所应执行的操作,在算法中都有确切的规定,不会产生二义性, 使算法的执行者或阅读者都能明确其含义及如何执行。
(3) 可行性 。算法中的所有操作都可以通过已经实现的基本操作运算执行有限次来实现。
(4) 输入 。一个算法有零个或多个输入。当用函数描述算法时,输入往往是通过形参表示的, 在它们被调用时,从主调函数获得输入值。
(5) 输出。
复杂度包括:时间复杂度与空间复杂度,通常我们更加看重一个算法的时间复杂度。
拿算法中最经典的高斯算法为例:
求 1~n 的和,有常规的算法:循环实现,与高斯算法,下面是代码实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 #include <iostream> using namespace std;int main () int n = 100 ; int sum = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { sum += i; } cout << sum; return 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 #include <iostream> using namespace std;int main () int n = 100 ; int sum = (1 + n) * n / 2 ; cout << sum; return 0 ; }
我们可以注意到,当使用常规算法时,需要执行的语句数会随着整数 n 的变化而变化,成线性相关,当 n 为一万时,那么 sum+=i; 这条语句需要执行的次数就是一万次。而使用高斯算法时,无论 n 的值是多少,sum = (1 + n) * n / 2; 都只会执行一次。
假设每条语句的执行时间都相同,设为 1,则使用常规算法消耗的时间大致可以认为是 n*1,高斯算法消耗的时间大概是 1。
我们通常使用大 O 表示法,来表示一个算法的复杂度,这里可以写为:常规算法 O (n),高斯算法 O (1)
需要注意的是,若是算法中使用了两个循环 (非嵌套),执行了 2n 条语句,我们仍然记为 O (n)
又或者使用了 2,3,4 条语句,只要这个算法的代码实现并不会随 n 变动,我们仍然记为 O (1)
因此,O (2n),O (3n),O (5),这些形式都是错误的。通常有以下几种表达式来描述时间复杂度:
O (1):常量阶
O (log n):对数阶
O (n):线性阶
O (n log n):线性对数阶
O(n2 ):二次方阶
O(2n ):指数阶
O (!n):阶乘阶
对于一个算法,比如排序一组数据:
1 int arr[] = {1 , 3 , 5 , 10 , 9 };
对于这组数据,显然只需要排序一次便能够得到有序数组,但是这并不代表使用的排序算法就是 O (1) 阶的,我们要按照最差的情况来估计,如果是冒泡排序,我们要按照每一次都需要排序来估计,第一次到第 n 次需要的执行的次数分别为 n-1 到 1,所以总执行次数为 n * (n - 1) / 2 也就是 1/2 * n^2 + 1/2 * n - 1/2 次,我们仅取其最大的部分,则冒泡排序的时间复杂度为 O (n2 ) 阶。
冒泡排序:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 #include <iostream> using namespace std;void maoPao (int * arr, int arrLen) for (int i = arrLen; i > 0 ; i--) { for (int j = 0 ; j < i - 1 ; j++) { if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1 ]) { int temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j + 1 ]; arr[j + 1 ] = temp; } } } } int main () int arr[] = { 10 , 9 , 5 , 3 , 1 }; maoPao (arr, 5 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) { cout << arr[i] << "\t" ; } return 0 ; }
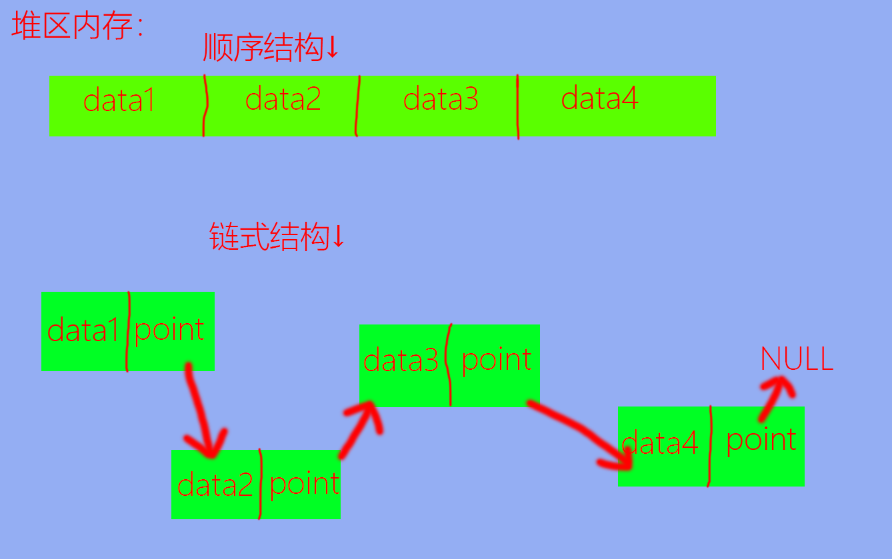
# 存储结构:存储结构大致可以分为两类:
顺序结构:在 物理内存中连续 ,并且在逻辑顺序上也连续 。链式结构:包含 数据域 与指针域 ,在物理内存中不一定连续 ,但在逻辑顺序上连续 。
其中,数据域用于存储数据,指针域用于存储后继元素的地址。
如图:
由图可以直观的看出二者的差别。
顺序结构与链式结构比较:
顺序结构的数据存储密度更高 ,占用空间更少,但是需要一段连续的空间 。
链式结构由于需要使用指针域保存与其关联的节点的地址,所以数据存储密度相对低 ,占用空间更多,但是由于分布存储的特点,并不需要一段连续的空间 。
顺序结构的插入与删除更加繁琐,时间复杂度为 O (n),但是顺序结构的修改,时间复杂度为 O (1)
链式结构的插入与删除,时间复杂度为 O (1),但是查找数据和修改数据,时间复杂度为 O (n)
# 线性结构: # 线性表 (List)线性表(List):零个或多个数据元素的有限序列。
线性表的数据集合为 {a1,a2,…,an},假设每个元素的类型均为 DataType。其中,除第一个元素 a1 外,每一个元素有且只有一个直接前驱元素,除了最后一个元素 an 外,每一个元素有且只有一个直接后继元素。数据元素之间的关系是一对一的关系。
在较复杂的线性表中,一个数据元素可以由若干个数据项组成。在这种情况下,常把数据元素称为记录 ,含有大量记录的线性表又称为文件
# 使用 C++ 实现顺序表:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 #pragma once #include <iostream> using namespace std;template <class T >class List { private : T* box; int m_size; int m_capacity; public : List () { this ->m_capacity = 2 ; this ->m_size = 0 ; this ->box = new T[this ->m_capacity]; } ~List () { if (this ->box != NULL ) { delete [] this ->box; this ->box = NULL ; } } void push_front (T val) if (this ->m_size == this ->m_capacity) { this ->m_capacity *= 2 ; T* temp = new T[this ->m_capacity]; for (int i = 0 ; i < this ->m_size; i++) { temp[i] = this ->box[i]; } delete [] this ->box; this ->box = temp; } for (int i = this ->m_size; i > 0 ; i--) this ->box[i] = this ->box[i - 1 ]; this ->box[0 ] = val; this ->m_size++; } void push_back (T val) if (this ->m_size == this ->m_capacity) { this ->m_capacity *= 2 ; T* temp = new T[this ->m_capacity]; for (int i = 0 ; i < this ->m_size; i++) { temp[i] = this ->box[i]; } delete [] this ->box; this ->box = temp; } this ->box[this ->m_size] = val; this ->m_size++; } void insert (int index, T val) if (this ->m_size == this ->m_capacity) { this ->m_capacity *= 2 ; T* temp = new T[this ->m_capacity]; for (int i = 0 ; i < this ->m_size; i++) { temp[i] = this ->box[i]; } delete [] this ->box; this ->box = temp; } for (int i = this ->m_size; i > index; i--) this ->box[i] = this ->box[i - 1 ]; this ->box[index] = val; this ->m_size++; } void popByIndex (int index) if (index < 0 || index > this ->m_size) { cout << "Index error" << endl; return ; } for (int i = index; i < this ->m_size - 1 ; i++) { this ->box[i] = this ->box[i + 1 ]; } this ->m_size--; } int size () return this ->m_size; } int capacity () return this ->m_capacity; } bool isEmpty () if (this ->m_size == 0 ) return true ; return false ; } int findByElem (T Elem) int index = -1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < this ->m_size; i++) { if (this ->box[i] == Elem) { index = i; break ; } } return index; } T getElemByIndex (int index) { if (index < 0 || index > this ->m_size) { cout << "Index error.Return head element!" << endl; return this ->box[0 ]; } return this ->box[index]; } void clear () this ->m_size = 0 ; } };
main 函数调试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 #include <iostream> #include "List.hpp" #include "testArr.h" using namespace std;int main () testArr ta; List<int > list; for (int i = 0 ; i < ta.arrLen; i++) { list.push_front (ta.arr[i]); } for (int i = 0 ; i < ta.arrLen; i++) { list.push_back (ta.arr[i]); } for (int i = 0 ; i < list.size (); i++) { cout << list.getElemByIndex (i) << "\t" ; } cout << "\n" ; list.popByIndex (0 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < list.size (); i++) { cout << list.getElemByIndex (i) << "\t" ; } cout << "\n" ; list.insert (1 , 100 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < list.size (); i++) { cout << list.getElemByIndex (i) << "\t" ; } cout << "\n" ; list.clear (); if (list.isEmpty ()) { cout << "已清空" << endl; } return 0 ; }
# 使用 C++ 实现单链表:单链表指指针域中仅仅保存单方向指向后继节点 的指针的链式存储线性表。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 #pragma once #include <iostream> using namespace std;template <class T >class Node {public : T data; Node* next; public : Node (T value) { this ->data = value; this ->next = NULL ; } ~Node () { if (this ->next != NULL ) { delete this ->next; this ->next = NULL ; } } }; template <class T >class Link {private : Node<T>* next; int size; Node<T>* end; public : Link () { this ->next = NULL ; this ->end = NULL ; this ->size = 0 ; } ~Link () { this ->next = NULL ; this ->end = NULL ; } void push_front (T value) if (this ->size == 0 ) { this ->next = new Node <T>(value); this ->end = this ->next; this ->size++; return ; } Node<T>* newNode = new Node <T>(value); newNode->next = this ->next; this ->next = newNode; this ->size++; } void push_back (T value) if (this ->size == 0 ) { this ->next = new Node <T>(value); this ->end = this ->next; this ->size++; return ; } this ->end->next = new Node <T>(value); this ->end = this ->end->next; this ->size++; } Node<T>* find (T key) { Node<T>* p = this ->next; for (int i = 0 ; p != NULL ; p = p->next) { if (p->data == key) { return p; } } return NULL ; } void pop_back () if (this ->size == 0 ) { return ; } Node<T>* np = this ->next; if (np == this ->end) { this ->next = NULL ; this ->end = NULL ; this ->size--; return ; } for (; np->next != end; np = np->next); np->next = NULL ; this ->end = np; this ->size--; } void pop_front () if (this ->size == 0 ) { return ; } this ->next = this ->next->next; this ->size--; } void pop_Node (Node<T>* node) if (node == NULL ) { cout << "pop error!" << endl; return ; } for (Node<T>* np = this ->next; np->next != NULL ; np = np->next) { if (np->next == node) { np->next = np->next->next; } } } void printLink () for (Node<T>* p = this ->next; p != NULL ; p = p->next) { cout << p->data << "\t" ; } } void clearLink () this ->next = NULL ; this ->end = NULL ; this ->size = 0 ; } };
main 函数调试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 #include <iostream> #include "Link.hpp" #include "testArr.h" using namespace std;int main () testArr ta; Link<int > link; for (int i = 0 ; i < ta.arrLen; i++) { link.push_back (ta.arr[i]); } for (int i = ta.arrLen - 1 ; i > -1 ; i--) { link.push_front (ta.arr[i]); } link.printLink (); cout << "\n" ; link.pop_Node (link.find (2 )); link.pop_front (); link.pop_back (); link.printLink (); cout << "\n" ; link.clearLink (); link.printLink (); return 0 ; }
# 栈 (Stack)特点: 先进后出 (FILO) (First in Last out)
栈的结构类似于电梯,先进去的元素会在栈底,后进去的元素会在栈顶,后进的元素会先出,先进的元素会后出。
如下图:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | | (栈顶) | | | | | | --------- (栈底) | | (存入数据时) | V | | DATA1先入栈,在栈底 | | DATA2后入栈,在栈顶 | DATA2 | DATA2会先出栈 | DATA1 | 随后DATA1才能出栈 ---------
# 使用 C++ 实现顺序栈:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 #pragma once #include <iostream> #include <stdlib.h> using namespace std;template <class T >class Stack { private : int size; int len; T* stack; public : Stack () { this ->len = 2 ; this ->size = 0 ; this ->stack = new T[this ->len]; } Stack (int len) { this ->len = len; this ->size = 0 ; this ->stack = new T[this ->len]; } ~Stack () { delete [] this ->stack; this ->stack = nullptr ; } int IsEmpty () if (this ->size == 0 ) return 1 ; return 0 ; } int Size () return this ->size; } T GetTop () { return this ->stack[this ->size - 1 ]; } void Push (T val) if (this ->size == this ->len) { this ->len *= 2 ; T* newSpace = new T[this ->len]; for (int i = 0 ; i < this ->size; i++) { newSpace[i] = this ->stack[i]; } delete [] this ->stack; this ->stack = newSpace; } this ->stack[this ->size] = val; this ->size++; } void Pop () if (this ->IsEmpty ()) return ; this ->size--; } };
main 函数调试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #include <iostream> #include "Stack.hpp" #include "testArr.h" using namespace std;int main () testArr ta; Stack<int > s; ta.printArr (); cout << endl; for (int i = 0 ; i < ta.arrLen; i++) { s.Push (ta.arr[i]); } for (int i = 0 ; i < ta.arrLen; i++) { cout << s.GetTop () << "\t" ; s.Pop (); } return 0 ; }
# 使用 C++ 实现链栈:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 #pragma #include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std;template <class T >class StackNode {public : T data; StackNode<T>* prior; StackNode (T val, StackNode* node = nullptr ) { this ->data = val; this ->prior = node; } ~StackNode () {}; }; template <class T >class LinkStack {private : StackNode<T>* top; int size; public : LinkStack () { this ->size = 0 ; this ->top = nullptr ; } int IsEmpty () if (this ->size == 0 ) return 1 ; return 0 ; } int Size () return this ->size; } T GetTop () { return this ->top->data; } void Push (T val) StackNode<T>* sn = new StackNode <T>(val, this ->top); this ->top = sn; this ->size++; } void Pop () if (this ->IsEmpty ()) return ; StackNode<T>* deln = this ->top; this ->top = this ->top->prior; delete deln; this ->size--; deln = nullptr ; } ~LinkStack () { while (this ->top) this ->Pop (); } };
main 函数调试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #include <iostream> #include "LinkStack.hpp" #include "testArr.h" using namespace std;int main () testArr ta; LinkStack<int > ls; ta.printArr (); cout << endl; for (int i = 0 ; i < ta.arrLen; i++) { ls.Push (ta.arr[i]); } for (int i = 0 ; i < ta.arrLen; i++) { cout << ls.GetTop () << "\t" ; ls.Pop (); } return 0 ; }
# 栈:进制转换问题:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 #include <iostream> #include "Stack.hpp" using namespace std;int main () int number = 180 ; Stack<int > stack; while (number != 0 ) { stack.Push (number % 2 ); number /= 2 ; } int stackLength = stack.Size (); for (int i = 0 ; i < stackLength; i++) { if (i % 4 == 0 ) cout << " " ; cout << stack.GetTop (); stack.Pop (); } }
# 队列 (Queue)特点: 先进先出 (FIFO) (First in First out)
类似于排队。仅能从队尾进入,队首离开。
# 使用 C++ 实现顺序循环队列:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 #pragma once #include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std;template <class T >class Queue {private : T* queue; int head; int rear; int size; int len; public : Queue () { this ->len = 2 ; this ->size = 0 ; this ->head = this ->rear = 0 ; this ->queue = new T[this ->len]; } Queue (int len) { this ->len = len; this ->size = 0 ; this ->head = this ->rear = 0 ; this ->queue = new T[this ->len]; } void Push (T val) if (this ->len == this ->size) { int length = this ->len; this ->len *= 2 ; T* newSpace = new T[this ->len]; int newIndex = this ->head; int index = this ->head; for (int i = 0 ; i < this ->size; i++) { newSpace[newIndex] = this ->queue[index]; newIndex = (newIndex + 1 ) % this ->len; index = (index + 1 ) % length; } delete [] this ->queue; this ->queue = newSpace; this ->rear = newIndex; } this ->queue[this ->rear] = val; this ->rear = (this ->rear + 1 ) % this ->len; this ->size++; } int IsEmpty () if (this ->size == 0 ) return 1 ; return 0 ; } T GetTop () { return this ->queue[head]; } int Size () return this ->size; } void Pop () if (IsEmpty ()) return ; this ->head = (this ->head + 1 ) % this ->len; this ->size--; } };
main 函数调试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #include <iostream> #include "Queue.hpp" #include "testArr.h" using namespace std;int main () testArr ta; Queue<int > q; ta.printArr (); cout << endl; for (int i = 0 ; i < ta.arrLen; i++) { q.Push (ta.arr[i]); } for (int i = 0 ; i < ta.arrLen; i++) { cout << q.Front () << "\t" ; q.Pop (); } return 0 ; }
# 使用 C++ 实现链式队列:# 队列:热土豆问题:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 #include <iostream> #include "Queue.hpp" #include "testArr.h" using namespace std;int main () Queue<string> q; string seed[] = { "张三" , "李四" , "王五" , "老六" , "头七" , "老八" , "九哥" }; for (int i = 0 ; i < 7 ; i++) { q.Push (seed[i]); } int number = 5 ; while (!q.IsEmpty ()) { for (int i = 1 ; i < number; i++) { string temp = q.Front (); q.Pop (); q.Push (temp); } cout << q.Front () << endl; q.Pop (); } return 0 ; }
# 队列:打印任务问题:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 #pragma once #include <iostream> using namespace std;class PrintProblem { public : bool free; float speed; public : PrintProblem (int type); void printType (int type) }; #include "PrintProblem.h" PrintProblem::PrintProblem (int type) { if (type == 1 ) this ->speed = 10.0 / 60 ; else this ->speed = 5.0 / 60 ; this ->free = true ; } void PrintProblem::printType (int type) if (type == 1 ) this ->speed = 10.0 / 60 ; else this ->speed = 5.0 / 60 ; } #include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <ctime> #include <cstdlib> #include "PrintProblem.h" using namespace std;struct printTask { int startTime; int printTime; int printPage; }; int main () int flag = 0 ; srand ((unsigned )time (NULL )); queue<struct printTask> printQueue; PrintProblem printer (1 ) ; queue<int > waitTime; while (flag < 3600 ) { if (rand () % 180 == 0 ) { struct printTask newTask; newTask.printPage = rand () % 20 + 1 ; newTask.startTime = flag; newTask.printTime = ceil (newTask.printPage / printer.speed); printQueue.push (newTask); } if (!printQueue.empty () && printer.free) { printer.free = false ; } if (!printer.free) { printQueue.front ().printTime--; if (printQueue.front ().printTime <= 0 ) { printer.free = true ; int finishTime = flag; waitTime.push (finishTime - printQueue.front ().startTime); printQueue.pop (); } } flag++; } float average = 0.0f ; int length = waitTime.size (); for (int i = 0 ; i < length; i++) { average += waitTime.front (); waitTime.pop (); } cout << "平均等待时间" << (average / length) << "s" << "还有" << printQueue.size () << "个打印任务未完成" << endl; return 0 ; }
# 双端队列 (Deque)# C++ 提供的双端队列:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 #include <iostream> #include <deque> using namespace std;int main () deque<type> dequeName; push_back (); push_front (); pop_back (); pop_front (); front (); back (); size (); empty (); return 0 ; }
# 双端队列:"回文词" 判断:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <deque> using namespace std;int main () deque<string> dQ; string huiWen[] = { "上" ,"海" ,"自" ,"来" ,"水" ,"来" ,"自" ,"海" , "上" }; int len = sizeof (huiWen) / sizeof (huiWen[0 ]); for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++) { dQ.push_front (huiWen[i]); } len = dQ.size () / 2 ; bool judge = true ; for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++) { if (dQ.front () == dQ.back ()) { dQ.pop_front (); dQ.pop_back (); } else judge = false ; } if (judge) cout << "该string为回文" << endl; else cout << "该string不是回文" << endl; return 0 ; }
# 散列表 (Hash Table / 哈希表)创建一个存储空间,每个位置有对应的槽号,将数据存储后,只需要通过槽号进行读取。
则可以实现时间复杂度为 O (1) 的查找速度。
我们将数据项占据的比例称为散列表的 "负载因子"。例如:
某散列表大小为 11,存储项共 6 个,则其负载因子为 6/11
冲突:指两项数据,通过散列函数计算后,得到相同的 Hash 值
# 散列函数(1) 求余散列函数:
假设散列表的总大小为 size,要存储的数据项为 item,则可以使用 h (item) = item % size
其中 h (item) 为 item 对应的存储槽号。若冲突,则将槽号向后顺延。
(2) 折叠散列函数:
将数据项按照位数分为若干段,再将几段数字相加,最后使用散列表大小求余,得到散列值。
(3) 平方取中散列函数:
先将数据项做平方运算,然后取平方数的中间两位。再对散列表大小求余。
# MD5 与 SHAMD5 与 SHA 都是为了实现散列表槽位计算而出现的散列表函数。
将任意数据进行 MD5 或 SHA 计算后,会获得相应的散列值 (MD5 计算出的 Hash 值为 128 位,SHA0 计算出的 Hash 值为 160 位)
使用 MD5 或 SHA 计算出的 Hash 值几乎不存在冲突的可能。
# 区块链技术区块链的发展得益于散列函数。
区块链是大规模的分布式数据库。
区块链的最本质特征是 "去中心化"。不存在任何控制中心、协调中心节点。所有的节点都是平等的,无法被控制。
区块链由一个个区块 (block) 组成,区块分为头 (head) 和体 (body)。
区块头记录了一些元数据和链接到前一个区块的信息:生成时间、前一个区块的散列值。
工作量证明 (Proof of Work):
由于区块链是大规模的分布式数据库,同步较慢,新区快的添加速度需要得到控制。
目前最大规模区块链 Bitcoin (比特币) 采用的速度是平均每 10 分钟生成一个区块。
# 处理冲突(1) 开放地址
将冲突的数据项向后顺延,或者跳跃式顺延。
如 data1 和 data2 同样对应 0,则 data1 存于 0,data2 顺延存于 1。
但是这种顺延方式,若是冲突较多,则会导致冲突数据大量集中。
因此可以采取跳跃式顺延解决。
如 data1 存于 0,data2 存于 0+skip,skip 可以是任意不可以整除表大小的数。如果 skip 可以整除表,则会有部分槽永远不会被顺延。
(2) 数据链
将槽位的存储空间扩大。
如 data1 和 data2 同样对应 0,则使用数组等方式,将之一起存入 0 槽位。
查找时使用顺序查找的方式,从而获取数据项。这是介于 O (1) 和 O (n) 之间的选择。
# C++ 提供的 map 类map 是 STL 的一个关联容器,它提供一对一的 hash。
第一个可以称为关键字 (key),每个关键字只能在 map 中出现一次;
第二个可能称为该关键字的值 (value);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <map> using namespace std;int main () map<keyType, valueType> mapName; map<int , string> mapStudent; begin (); end (); rbegin (); rend (); cbegin (); cend (); crbegin (); crend (); find (key); lower_bound (key); upper_bound (key); equal_range (key); empty (); size (); max_size (); operator []; at (key); insert ({key,value}); erase (); swap (); clear (); emplace (); emplace_hint (); count (key); return 0 ; }
# 算法 # 递归 (Recursion)递归:指函数自我调用,分解问题,解决问题。
1. 存在一个大规模问题,可以被分解为小规模问题。
2. 小规模问题存在简单的解决方法。
3. 将小规模问题的结果汇总,得到大规模问题的解。
# 递归:冒泡排序 (递归实现)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 void Sort::bubbleSort (int * arr, int arrLen) arrLen--; if (arrLen <= 0 ) return ; for (int i = 0 ; i < arrLen; i++) { if (arr[i] > arr[i + 1 ]) { int temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[i + 1 ]; arr[i + 1 ] = temp; } } bubbleSort (arr, arrLen); } int main () int arr[10 ] = { 1 ,6 ,7 ,3 ,5 ,6 ,9 ,0 ,4 ,5 }; Sort sort; sort.bubbleSort (arr, 10 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { cout << arr[i] << endl; } return 0 ; }
# 贪心策略 (Greedy Method)优化问题:找到一个问题的最优解。
例如:在一个城市中,找到从 A 地到 B 地的最优路线。
# 贪心:找零问题# 动态规划 (Dynamic Planning)# 动态规划:背包问题现有 5 个物品,背包仅能负重 20 公斤,如何选取最高价值的物品?
item
weight
value
1
2
3
2
3
4
3
4
8
4
5
8
5
9
10
思路: 记 m (i,W) 为:前 i (1 <= i <= 5) 个宝物中,组合不超过 W (1 <= W <= 20) 重量,得到的最大价值 m (i,W) 应该取 m (i-1, W) 和 m (i-1, W-Wi )+vi 其中价值更高的值
则可以绘制动态规划表:
m(i\W)
0
1
2
3
4
5
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
3
3
3
3
2
0
0
3
4
4
7
3
0
0
3
4
8
8
4
0
0
3
4
8
8
5
0
0
3
4
8
8
由公式可知:m (5,5) = m (4,5) = max {m (3,5), m (3,0) + 8}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 #include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std;#define MAX_I 6 #define MAX_W 21 struct object { int w; int v; }; int max (int a, int b) if (a > b) return a; else return b; } int main () vector<object> tr; int wArr[5 ] = { 2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,9 }; int vArr[5 ] = { 3 ,4 ,8 ,8 ,10 }; for (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) { object temp; temp.w = wArr[i]; temp.v = vArr[i]; tr.push_back (temp); } int m[MAX_I][MAX_W]; for (int i = 0 , w = 0 ; w < MAX_W; w++) { m[i][w] = 0 ; } for (int w = 0 , i = 0 ; i < MAX_I; i++) { m[i][w] = 0 ; } for (int i = 1 ; i < MAX_I; i++) { for (int w = 1 ; w < MAX_W; w++) { if (tr[i - 1 ].w > w) m[i][w] = m[i - 1 ][w]; else m[i][w] = max (m[i - 1 ][w],m[i - 1 ][w - tr[i - 1 ].w] + tr[i - 1 ].v); } } cout << m[5 ][20 ] << endl; return 0 ; }
# 查找 (Search)# 顺序查找 (Sequential Search)从数据头,向后逐个比对。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 #include "Search.h" int Search::sequentialSearch (vector<int >& arr, int item, int arrLen) int pos = 0 ; while (pos < arrLen) { if (arr[pos] == item) return pos; pos++; } return -1 ; }
# 二分查找 (Binary Search)二分查找基于二分法,仅能用于有序表。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 #include "Search.h" int Search::binarySearch (vector<int >& arr, int item, int arrLen) int left = 0 , right = arrLen - 1 ; while (left <= right) { int mid = (left + right) / 2 ; if (arr[mid] == item) return mid; if (item < arr[mid]) right = mid - 1 ; else left = mid + 1 ; } return -1 ; }
# 排序 (Sort)# 冒泡排序 (Bubble Sort)仅将相邻的两项进行排序。
当首次冒泡后,最大项会被置于最后 (升序)。则下一次只需对前 n-1 个数排序。
以此类推,直到 n=2。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 #include "Sort.h" void Sort::bubbleSort (vector<int >& arr) for (int i = arr.size () - 1 ; i > 0 ; i--) { for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++) { if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1 ]) { int temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j + 1 ]; arr[j + 1 ] = temp; } } } }
冒泡算法改进:
如果一次排序中,没有任何数的位置发生改变,则说明已经排序完成,可以直接返回
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 #include "Sort.h" void Sort::bubbleSort (vector<int >& arr) for (int i = arr.size () - 1 ; i > 0 ; i--) { bool exchange = false ; for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++) { if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1 ]) { exchange = true ; int temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j + 1 ]; arr[j + 1 ] = temp; } } if (!exchange) return ; } }
# 选择排序 (Selection Sort)在冒泡排序的思想上,对交换进行优化。
仍然进行多次对比,但不交换,记录最大项所在位置,最后再进行交换
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 #include "Sort" void Sort::selectionSort (vector<int >& arr) for (int i = arr.size (); i > 0 ; i--) { int maxIndex = 0 ; for (int j = 1 ; j < i; j++) { if (arr[j] > arr[maxIndex]) maxIndex = j; } int temp = arr[i - 1 ]; arr[i - 1 ] = arr[maxIndex]; arr[maxIndex] = temp; } }
# 插入排序 (Insertion Sort)插入排序维持一个已经排好序的子列表,其位置始终在列表的前部,然后逐步扩大这个子列表直到全表。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 #include "Sort" void Sort::insertionSort (vector<int >& arr) int index; int currentValue; for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.size (); i++) { currentValue = arr[i]; index = i; while (index > 0 && arr[index - 1 ] > currentValue){ arr[index] = arr[index - 1 ]; index--; } arr[index] = currentValue; } }
# 谢尔排序 (Shell Sort)假设将数组 {6,5,4,3,2,1,9,8,7} 进行排序 (升序)。
则可以将其划分为三个子数组,为 {6,5,4}、{3,2,1}、
然后分别对其进行插入排序,变为
可以发现,虽然并未变成完全有序,但是相对于原数组,是更有序的。
假设现有 n 个数需要进行排序。可以将其划分为 n / 2 个子数组进行排序
对排序后的数组再划分为 n / 4 个子数组进行排序,以此类推,直到 n / … 为 1 时,即为插入排序。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 #include "Sort.h" void gapInsertionSort (vector<int >& arr, int start, int gap) for (int i = start + gap; i < arr.size (); i += gap) { int currentValue = arr[i]; int index = i; while (index >= gap && arr[index - gap] > currentValue) { arr[index] = arr[index - gap]; index = index - gap; } arr[index] = currentValue; } } void Sort::shellSort (vector<int >& arr) int subCount = arr.size () / 2 ; while (subCount > 0 ) { for (int start = 0 ; start < subCount; start++) gapInsertionSort (arr, start, subCount); subCount /= 2 ; } }
# 归并排序 (Merge Sort)归并排序是一种递归算法
思路是将数据表持续分裂为两半,并对两半分别进行排序。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 #include "Sort.h" void Sort::mergeSort (vector<int >& arr) if (arr.size () > 1 ) { int mid = arr.size () / 2 ; vector<int > leftHalf (arr.begin(), arr.begin() + mid) ; vector<int > rightHalf (arr.begin() + mid, arr.end()) ; mergeSort (leftHalf); mergeSort (rightHalf); int i = 0 , j = 0 , k = 0 ; while (i < leftHalf.size () && j < rightHalf.size ()) { if (leftHalf[i] < rightHalf[j]) { arr[k] = leftHalf[i]; i++; } else { arr[k] = rightHalf[j]; j++; } k++; } while (i < leftHalf.size ()) { arr[k] = leftHalf[i]; i++; k++; } while (j < rightHalf.size ()) { arr[k] = rightHalf[j]; j++; k++; } } }
# 快速排序 (Quick Sort)找到数据表的中值,并将数据表分为两半,随后自我调用,直到数据表仅有 1 项数据。
寻找中值:
1. 定义左标与右标,假设第一个值为中值,将左标向右移动,遇到第一个大于中值的项时停止。
2. 将右标向左移动,遇到第一个小于中值的项时停止。
3. 将左标与右标指向的值交换。随后继续重复左标右移,右标左移的步骤。
4. 当左标超过右标时,此时右标指向的值即为中值需要交换的位置。则可将中值与右标指向的值交换。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 #include "Sort.h" int getMidI (vector<int >& arr, int first, int last) int midValue = arr[first]; int leftMark = first + 1 ; int rightMark = last; while (true ) { while (leftMark <= rightMark && arr[leftMark] <= midValue) leftMark++; while (rightMark >= leftMark && arr[rightMark] >= midValue) rightMark--; if (rightMark < leftMark) break ; else { int temp = arr[leftMark]; arr[leftMark] = arr[rightMark]; arr[rightMark] = temp; } } int temp = arr[first]; arr[first] = arr[rightMark]; arr[rightMark] = temp; return rightMark; } void quickSortHelper (vector<int >& arr, int first, int last) if (first < last) { int midValue = getMidI (arr,first,last); quickSortHelper (arr, first, midValue - 1 ); quickSortHelper (arr, midValue + 1 , last); } } void Sort::quickSort (vector<int >& arr) quickSortHelper (arr, 0 , arr.size () - 1 ); }